In the dynamic landscape of business, crises are inevitable. Whether it’s a financial downturn, a public relations nightmare, or a global pandemic, effective crisis management is crucial for an organization’s survival and recovery. In this article, we delve into strategies that businesses can employ to navigate and mitigate the impact of crises.
Introduction
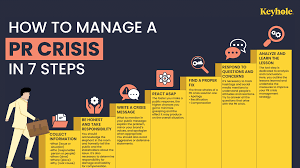
Crisis management is the process of preparing for, responding to, recovering from, and learning from a crisis situation. While each crisis is unique, having a robust framework in place enables businesses to respond promptly, minimize damage, and emerge stronger in the aftermath.
Preemptive Planning
- Risk Assessment: Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential crises. Assess the probability and potential impact of each scenario to prioritize preparedness efforts.
- Crisis Response Team: Assemble a dedicated crisis response team with representatives from various departments. Clearly define roles and responsibilities, ensuring a swift and coordinated response during a crisis.
- Communication Protocols: Establish clear communication protocols, including designated spokespersons and channels. Define how information will be disseminated internally and externally, maintaining transparency and accuracy.
Rapid Response
- Immediate Action Plan: Have an immediate action plan in place for the initial stages of a crisis. Swift decision-making and execution are crucial to gaining control and preventing escalation.
- Coordination and Communication: Ensure seamless coordination among the crisis response team. Timely and accurate communication internally and externally helps manage perceptions and reduces uncertainty.
- Adaptability: Be adaptable in responding to evolving situations. A flexible approach allows organizations to adjust strategies based on real-time developments during a crisis.
Reputation Management
- Transparent Communication: Transparency is key to maintaining trust. Keep stakeholders informed about the situation, steps being taken, and the expected outcomes. Acknowledge mistakes and communicate corrective measures.
- Media Management: Develop a media management strategy to control the narrative. Anticipate potential questions and prepare key messages to convey a consistent and reassuring message.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engage with stakeholders, including customers, employees, investors, and the community. Address concerns, provide updates, and demonstrate a commitment to resolving issues.
Recovery and Learning
- Post-Crisis Evaluation: Conduct a comprehensive evaluation post-crisis to assess the effectiveness of the response. Identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement in the crisis management plan.
- Adaptive Strategies: Use insights gained from the crisis to adapt and strengthen the organization’s crisis management strategies. Implement changes to enhance preparedness for future unforeseen events.
- Employee Support: Provide support and resources to employees who may have been affected by the crisis. Employee well-being is crucial for organizational recovery and resilience.
Technological Integration
- Crisis Management Tools: Utilize technology to streamline crisis management processes. Implement tools for real-time communication, data analysis, and monitoring, enhancing the efficiency of response efforts.
- Data Security Measures: In cases of cyber threats or data breaches, prioritize data security measures. Safeguarding sensitive information is essential for maintaining trust and minimizing long-term damage.
- Digital Communication Platforms: Leverage digital communication platforms to disseminate information quickly and reach a wide audience. Social media, email, and other digital channels can be powerful tools for crisis communication.
Collaborative Partnerships
Government and Industry Collaboration: Collaborate with government bodies, industry partners, and relevant organizations. Shared resources and information exchange can strengthen the collective response to a crisis.
- Crisis Simulation Exercises: Conduct regular crisis simulation exercises involving internal and external stakeholders. These exercises help test the effectiveness of crisis management strategies and identify areas for improvement.
- Mutual Support Networks: Establish mutual support networks with other businesses in the industry. Shared experiences and collaborative problem-solving can enhance resilience during challenging times.
Conclusion
Effective crisis management is not just about reacting to unforeseen events but proactively preparing for them. By implementing preemptive planning, swift response mechanisms, reputation management strategies, and a commitment to continuous learning, businesses can navigate crises successfully. Technological integration, collaborative partnerships, and a focus on employee well-being contribute to an organization’s resilience and ability to emerge stronger from challenging situations.