Introduction
As we stand on the cusp of a new era in connectivity, the future of telecommunications is poised to leapfrog existing technologies with the advent of 6G and beyond. This article explores the trajectory of telecommunications, delving into the potential of 6G networks and the transformative technologies that may redefine the way we connect and communicate.
From 1G to 5G
The evolution of telecommunications has witnessed significant milestones, from the introduction of the first-generation (1G) analog networks to the current state-of-the-art 5G networks. Each generation brought advancements in speed, capacity, and connectivity, setting the stage for the next leap forward.
5G’s Impact on Connectivity
The deployment of 5G networks marked a revolutionary shift, unlocking unprecedented data speeds, lower latency, and the ability to connect a massive number of devices simultaneously. However, the demand for faster, more reliable, and ubiquitous connectivity continues to drive innovation.
Beyond 5G
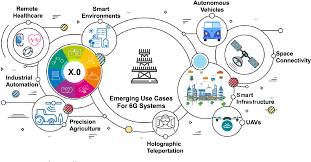
6G represents the next phase in the evolution of telecommunications, promising advancements that go beyond the capabilities of 5G. Envisioned to be an ultra-fast, intelligent, and hyper-connected network, 6G aims to address the growing demands of an increasingly digitized and interconnected world.
Anticipated Features of 6G
Unprecedented Speeds: 6G is expected to achieve data speeds several times faster than 5G, potentially reaching terabits per second. This would facilitate real-time communication, high-definition content streaming, and immersive augmented reality experiences.
Ultra-Low Latency: Reducing latency to the order of microseconds is a key goal of 6G. This ultra-low latency is crucial for applications like autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and other time-sensitive tasks.
Increased Device Density: 6G aims to support a significantly higher number of connected devices per square kilometer. This is essential for the proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT) and the seamless integration of smart devices into daily life.
Energy Efficiency: As the number of connected devices continues to rise, 6G strives for enhanced energy efficiency. New technologies, such as advanced power management and sustainable infrastructure, will play a crucial role.
Terahertz Frequency Bands
6G is expected to leverage terahertz frequency bands, offering higher bandwidths and enabling faster data transmission. This spectrum expansion comes with its own set of engineering challenges, including propagation and absorption issues.
Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces
Intelligent reflecting surfaces, or meta-surfaces, are anticipated to be a key technology in 6G. These surfaces can manipulate radio waves, optimizing signal strength and coverage, and mitigating obstacles and interference.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
The enhanced speed and ultra-low latency of 6G could revolutionize AR and VR applications. From immersive gaming experiences to advanced medical simulations, 6G has the potential to redefine how we interact with digital environments.
Autonomous Systems and AI
6G’s capabilities are poised to propel the development of autonomous systems, including self-driving cars and drones. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with 6G networks could lead to real-time decision-making and enhanced machine learning applications.
Technical Hurdles
The implementation of 6G faces technical challenges, including the optimization of terahertz frequencies, managing interference, and ensuring seamless handovers between different network nodes.
Global Standards and Collaboration
Establishing global standards for 6G is a critical consideration. Collaboration among industry stakeholders, governments, and standardization bodies is essential to ensure interoperability and a cohesive global framework.
Quantum Communication
Looking further into the future, beyond 6G, quantum communication holds promise as the next frontier. Quantum networks could offer unprecedented security and communication speeds by leveraging the principles of quantum entanglement.
Space-Based Connectivity
Space-based networks, using satellite constellations, may become integral to global connectivity. Companies are exploring the deployment of satellite mega-constellations to extend coverage to remote areas and enhance the resilience of telecommunications infrastructure.
Conclusion
The future of telecommunications is an exciting journey into an era of connectivity that transcends current boundaries. With 6G on the horizon, we anticipate not just faster speeds but a transformative shift in how we communicate, interact with technology, and envision the possibilities of a hyper-connected world.