Introduction
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has emerged as a revolutionary technology with transformative applications across various industries. In the healthcare sector, 3D printing is making significant strides, offering innovative solutions that are reshaping patient care and medical practices.
Revolutionizing Medical Imaging and Preoperative Planning
Utilizing 3D Printing for Creating Anatomical Models
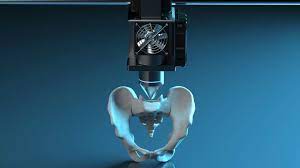
3D printing is revolutionizing medical imaging by allowing the creation of intricate anatomical models. This section explores how healthcare professionals use 3D-printed models to gain deeper insights into patient anatomy, facilitating better understanding and communication among medical teams.
Enhancing Preoperative Planning Through 3D-Printed Models
The impact of 3D printing on preoperative planning is profound. We delve into how surgeons leverage 3D-printed models to simulate and plan complex procedures, resulting in increased precision, reduced surgical risks, and improved patient outcomes.
Customized and Patient-Specific Implants
The Role of 3D Printing in Manufacturing Personalized Implants
Traditional implants may not always perfectly suit individual patients. This part discusses how 3D printing enables the creation of customized implants tailored to the specific anatomical features of each patient, leading to more successful surgeries and reduced complications.
Advantages of Patient-Specific Implants in Surgeries
Patient-specific implants offer numerous advantages, including better fit, reduced recovery times, and improved overall patient satisfaction. We explore the impact of 3D-printed implants in enhancing the efficacy of various surgical procedures.
Prosthetics and Orthopedic Devices
Crafting Custom Prosthetics Using 3D Printing
3D printing has transformed the field of prosthetics by allowing the production of custom-fitted and cost-effective prosthetic devices. This section highlights how 3D-printed prosthetics provide amputees with more comfortable and functional solutions.
Innovations in Orthopedic Devices Through Additive Manufacturing
Orthopedic devices, such as braces and supports, benefit from 3D printing’s ability to create intricate structures. We discuss how this technology is driving innovation in orthopedics, offering patients more personalized and efficient solutions.
Drug Formulation and Delivery
3D Printing’s Contribution to Personalized Drug Formulations
Personalized medicine is advancing with 3D printing, enabling the formulation of drugs tailored to individual patient needs. This part explores how this approach enhances treatment efficacy and minimizes side effects.
Advantages of 3D-Printed Drug Delivery Systems
The design flexibility of 3D printing extends to drug delivery systems. We discuss the advantages of 3D-printed drug delivery devices, including controlled release mechanisms and improved patient adherence.
Dental Applications and Prosthodontics
Transforming Dentistry with 3D-Printed Dental Models
Dentistry benefits immensely from 3D printing, particularly in the creation of precise dental models. This section explores how 3D-printed dental models enhance diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning.
Customized Prosthodontic Solutions Through Additive Manufacturing
Prosthodontics, including crowns and bridges, witness customization through 3D printing. We delve into how this technology is revolutionizing dental prosthetics, offering patients tailored solutions with enhanced aesthetics and functionality.
Bioprinting for Tissue Engineering
Advancements in Bioprinting Technology
The frontier of 3D printing extends to bioprinting, where living tissues are created layer by layer. This part discusses the advancements in bioprinting technology and its potential for revolutionizing organ transplantation and tissue engineering.
The Potential of 3D-Printed Tissues and Organs
Bioprinting holds the promise of addressing organ shortages by enabling the creation of functional tissues and organs. We explore the potential applications of 3D-printed tissues and organs in transplantation and regenerative medicine.
Cost-Efficiency and Time Savings in Healthcare
The Economic Benefits of 3D Printing in Healthcare
3D printing brings economic advantages to healthcare by reducing production costs and minimizing material wastage. This section discusses how the cost-efficiency of 3D printing contributes to making healthcare solutions more accessible.
Time-Saving Aspects in Surgeries and Medical Interventions
The efficiency of 3D printing translates into time savings in various medical procedures. We explore how rapid prototyping and the production of customized medical devices contribute to streamlined surgeries and interventions.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Addressing Challenges Associated with 3D Printing in Healthcare
While 3D printing offers numerous benefits, challenges exist, including material safety and regulatory concerns. This part explores the challenges associated with 3D printing in healthcare and potential strategies for mitigating them.
Ethical Considerations in the Use of 3D-Printed Medical Solutions
Ethical considerations are paramount in the development and use of 3D-printed medical solutions. We discuss ethical implications related to patient consent, privacy, and the equitable distribution of advanced healthcare technologies.
Regulatory Landscape and Standardization
Current Regulatory Frameworks for 3D-Printed Medical Devices
As 3D printing in healthcare expands, regulatory frameworks must adapt. This section provides an overview of current regulations governing 3D-printed medical devices and the evolving landscape of approvals and standards.
The Need for Standardization in the 3D Printing Healthcare Sector
Standardization is critical for ensuring the quality and safety of 3D-printed medical products. We explore the importance of establishing standardized processes, materials, and guidelines to foster confidence in 3D printing applications.
Training and Education in Medicine
Integrating 3D Printing Into Medical Education
3D printing is becoming an integral part of medical education. We discuss how incorporating 3D-printed models into medical training enhances the learning experience and prepares healthcare professionals for complex surgical scenarios.
Training Healthcare Professionals Using 3D-Printed Models
Hands-on training with 3D-printed models allows healthcare professionals to hone their skills in a risk-free environment. This part explores the practical applications of 3D printing in training surgeons, radiologists, and other medical specialists.
Global Adoption and Accessibility
The Global Impact of 3D Printing on Healthcare Accessibility
3D printing has the potential to address healthcare disparities globally. We explore initiatives and projects that leverage 3D printing to improve healthcare accessibility, especially in resource-limited regions.
Initiatives Promoting the Widespread Adoption of 3D Printing in Healthcare
Various initiatives and collaborations drive the adoption of 3D printing in healthcare. This section highlights efforts aimed at promoting knowledge sharing, technology transfer, and capacity building to expand the reach of 3D printing solutions.
Future Trends and Innovations
Anticipated Advancements in 3D Printing Technology for Healthcare
The future of 3D printing in healthcare holds exciting possibilities. We explore anticipated advancements in technology, including faster printing processes, new biocompatible materials, and enhanced precision in medical applications.
Emerging Trends Shaping the Future of 3D Printing in Healthcare
Emerging trends are shaping the trajectory of 3D printing in healthcare. This part discusses trends such as point-of-care printing, telemedicine applications, and collaborative research initiatives that will influence the future landscape.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Highlighting Notable Cases and Success Stories in 3D Printing Healthcare Applications
Real-world examples showcase the impact of 3D printing on healthcare outcomes. We highlight case studies and success stories that demonstrate how this technology has improved patient care, surgical outcomes, and treatment efficacy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the impact of 3D printing on healthcare solutions is transformative, offering personalized, cost-effective, and innovative approaches to patient care. As the technology continues to evolve, its integration into various medical disciplines holds the promise of revolutionizing the way healthcare is delivered and experienced.
FAQs
- How does 3D printing revolutionize medical imaging and preoperative planning?
- 3D printing revolutionizes medical imaging by enabling the creation of detailed anatomical models. In preoperative planning, surgeons use 3D-printed models to simulate procedures, enhancing precision and reducing surgical risks.
- What role does 3D printing play in creating customized implants?
- 3D printing allows the creation of customized implants tailored to individual patients. This technology ensures a better fit, reduces recovery times, and minimizes complications in various surgical procedures.
- How has 3D printing impacted the field of prosthetics?
- 3D printing has transformed prosthetics by enabling the production of custom-fitted and cost-effective devices. Patients benefit from more comfortable and functional solutions tailored to their unique anatomical features.
- What are the advantages of 3D-printed drug delivery systems?
- 3D-printed drug delivery systems offer advantages such as controlled release mechanisms and personalized formulations. This enhances treatment efficacy, minimizes side effects, and improves patient adherence.
- How does 3D printing contribute to dental applications and prosthodontics?
- 3D printing transforms dentistry by creating precise dental models and customized prosthodontic solutions. This technology enhances diagnostic accuracy, treatment planning, and the overall quality of dental care.