Introduction
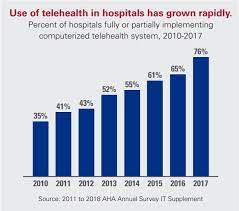
The landscape of healthcare is undergoing a transformative shift with the rapid rise of telehealth services. Accelerated by technological advancements and the global need for accessible healthcare, telehealth has become a critical component of the healthcare ecosystem. This article explores the key factors contributing to the rise of telehealth services, the benefits they offer, and the potential impact on the future of healthcare delivery.
Technological Advancements Driving Telehealth
1. Ubiquity of Smart Devices
The widespread use of smartphones, tablets, and other smart devices has created a platform for accessible and convenient telehealth services. Patients can connect with healthcare providers from the comfort of their homes, eliminating the need for physical visits to medical facilities.
2. High-Speed Internet Connectivity
The expansion of high-speed internet infrastructure has facilitated seamless video consultations and remote monitoring. Improved connectivity ensures that telehealth services can deliver real-time interactions, diagnostic assessments, and ongoing care with minimal disruptions.
Key Components of Telehealth Services
1. Telemedicine Consultations
Telemedicine consultations enable patients to connect with healthcare professionals remotely. Video calls, audio calls, and secure messaging platforms provide effective means of communication for routine check-ups, follow-up appointments, and general medical advice.
2. Remote Patient Monitoring
Technological devices such as wearable sensors and connected medical equipment enable remote monitoring of patients’ vital signs, chronic conditions, and overall health. This real-time data allows healthcare providers to assess patients’ well-being without physical presence.
Benefits of Telehealth Services
1. Increased Accessibility
Telehealth services break down geographical barriers, making healthcare accessible to individuals in remote or underserved areas. Patients no longer need to travel long distances for routine consultations, improving healthcare access for all.
2. Convenience and Time Efficiency
Telehealth offers unparalleled convenience for both patients and healthcare providers. Virtual consultations save time, reduce waiting room congestion, and allow for flexible scheduling, enabling individuals to seek medical advice without disrupting their daily routines.
3. Reduced Healthcare Costs
Telehealth services can contribute to cost savings for both patients and healthcare systems. By minimizing the need for in-person visits and associated expenses, such as transportation and facility maintenance, telehealth helps streamline healthcare delivery.
4. Early Detection and Intervention
Remote patient monitoring facilitates early detection of health issues and allows for timely intervention. Continuous monitoring of chronic conditions, for example, enables healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans promptly, reducing the risk of complications.
Challenges and Considerations
1. Technological Barriers
While technological advancements drive telehealth, barriers such as limited access to smart devices and reliable internet connectivity persist, especially in certain demographics and regions. Addressing these disparities is crucial for ensuring equitable healthcare access.
2. Data Security and Privacy Concerns
The transmission and storage of sensitive health data during telehealth interactions raise concerns about data security and privacy. Adhering to robust encryption protocols and privacy regulations is essential to maintain patient trust and confidentiality.
The Future Landscape of Telehealth
1. Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The integration of AI in telehealth services holds the potential to enhance diagnostic capabilities, personalize treatment plans, and optimize healthcare delivery. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets to support healthcare providers in making more informed decisions.
2. Expanded Specialized Services
Telehealth is evolving to cover an increasing array of specialized services, including mental health consultations, dermatology assessments, and chronic disease management. This expansion broadens the scope of conditions that can be effectively addressed through virtual healthcare interactions.
Conclusion
The rise of telehealth services represents a paradigm shift in healthcare delivery, offering a blend of accessibility, convenience, and cost-effectiveness. As technology continues to advance and healthcare systems adapt, telehealth is poised to play an increasingly prominent role in providing quality healthcare services to individuals worldwide. While challenges persist, the transformative potential of telehealth services in improving patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency is undeniable. The future of healthcare is being shaped by the seamless integration of technology and compassionate, patient-centric virtual care.