Introduction to Decision-Making in Business
Decision-making is a fundamental aspect of business management, encompassing the process of selecting among alternative courses of action to achieve organizational goals and objectives. In this article, we explore the science of decision-making in business and strategies for making effective decisions in a complex and dynamic environment.
Understanding the Science of Decision-Making
The science of decision-making draws upon various disciplines, including psychology, economics, neuroscience, and organizational behavior, to understand the cognitive processes, biases, and heuristics that influence human decision-making in business contexts.
Factors Influencing Decision-Making in Business
Decision-making in business is influenced by a multitude of factors, including individual preferences, organizational goals, environmental constraints, market dynamics, stakeholder expectations, and risk considerations, shaping the decision-making process and outcomes.
Key Principles of Effective Decision-Making
Rationality and Logic
Effective decision-making in business requires rationality and logic, involving systematic analysis, evaluation, and comparison of alternatives based on objective criteria and evidence rather than emotions or personal biases.
Risk Assessment and Management
Risk assessment and management are integral to decision-making, as businesses must weigh the potential benefits and drawbacks of each option, anticipate uncertainties and contingencies, and implement strategies to mitigate risks and maximize rewards.
Information Processing and Analysis
Sound decision-making relies on accurate and relevant information, necessitating effective information gathering, processing, and analysis to identify patterns, trends, and insights that inform decision-making and reduce uncertainty.
Cognitive Biases and Heuristics
Understanding cognitive biases and heuristics is crucial for mitigating decision-making errors and distortions, as individuals may exhibit biases such as confirmation bias, anchoring bias, or overconfidence, leading to suboptimal decisions.
Strategies for Improving Decision-Making in Business
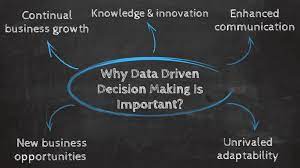
Data-Driven Decision-Making
Embrace data-driven decision-making approaches, leveraging data analytics, business intelligence, and predictive modeling to inform decision-making, identify opportunities, and optimize outcomes based on empirical evidence and insights.
Collaborative Decision-Making
Promote collaborative decision-making processes that involve stakeholders from diverse backgrounds, perspectives, and expertise, fostering creativity, innovation, and buy-in while mitigating groupthink and biases.
Scenario Planning and Simulation
Utilize scenario planning and simulation techniques to anticipate future scenarios, test assumptions, and evaluate the potential impacts of different decisions under various conditions, enabling proactive decision-making and risk management.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Foster a culture of continuous learning and adaptation, encouraging experimentation, reflection, and feedback to refine decision-making processes, learn from successes and failures, and adapt strategies in response to changing circumstances.
Benefits of Effective Decision-Making in Business
Improved Performance and Efficiency
Effective decision-making leads to improved performance and efficiency, as businesses can make timely, informed, and strategic decisions that align with organizational goals and priorities, driving productivity and profitability.
Enhanced Innovation and Creativity
Sound decision-making fosters innovation and creativity by encouraging experimentation, risk-taking, and exploration of new ideas and opportunities, fueling growth, differentiation, and competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Risk Mitigation and Resilience
By identifying and addressing risks proactively, effective decision-making enhances resilience and adaptability, enabling businesses to navigate challenges, crises, and disruptions with agility and confidence, minimizing negative impacts and maximizing recovery.
Competitive Advantage and Growth
Businesses that excel in decision-making gain a competitive advantage and drive sustainable growth by capitalizing on opportunities, anticipating market trends, and outperforming competitors through superior strategic execution and operational excellence.
Challenges and Considerations
Complexity and Uncertainty
Decision-making in business is fraught with complexity and uncertainty, requiring leaders to navigate ambiguous and dynamic environments, make decisions under pressure, and balance competing priorities and interests.
Time Constraints and Pressure
Time constraints and pressure can hinder effective decision-making, leading to rushed or impulsive decisions, overlooking critical information, or deferring decisions to avoid risk or conflict, necessitating discipline, prioritization, and delegation to manage time effectively.
Overcoming Cognitive Biases
Overcoming cognitive biases requires self-awareness, critical thinking, and deliberate efforts to challenge assumptions, seek diverse perspectives, and question preconceived notions, fostering a culture of openness, inquiry, and intellectual humility.
Balancing Intuition and Analysis
Balancing intuition and analysis is essential for effective decision-making, as intuition can provide valuable insights and gut feelings, but it must be complemented by analytical rigor, evidence-based reasoning, and structured decision-making processes to mitigate biases and errors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the science of decision-making in business is a multifaceted and dynamic field that encompasses cognitive processes, biases, and strategies for making effective decisions in complex and uncertain environments. By embracing key principles, strategies, and considerations, businesses can improve decision-making outcomes, enhance performance and resilience, and achieve sustainable growth and success in today’s competitive landscape.